Metadata Management
1. Overview
"Metadata Management" is the data management module in the system, which is the place to unify the management of metadata.
TapDB adopts metadata pre-registration mode. Before receiving the data reported by SDK, the events and attributes to be collected must be registered into the corresponding function module, and when receiving the data, the system needs to check the metadata according to the pre-registered metadata, and the data that meet the conditions will be stored, and the data that do not meet the conditions will be rejected.
This model can effectively improve the accuracy of data, and this model can solve the problem of inconsistent data reporting and data storage.
Metadata management consists of 3 parts: event management, event attribute management and user attribute management.
2. Applicable Roles and Uses
| Roles | Usage |
|---|---|
| Administrator | Entering buried scenarios and managing system metadata |
| Business person | View metadata and understand business implications of data |
| Client / Front End Engineer | View buried requirements |
3. Event Management
"Event" is the basic analysis object of various data analysis models in the system, and the system has built-in "preset events" and provides the function of reporting "custom events".
In the "Event Management" function, you can pre-register "custom events" before reporting, and manage "events" from various aspects.
Developers can check the pre-registered custom events that have been reported as "No" and perform buried development.
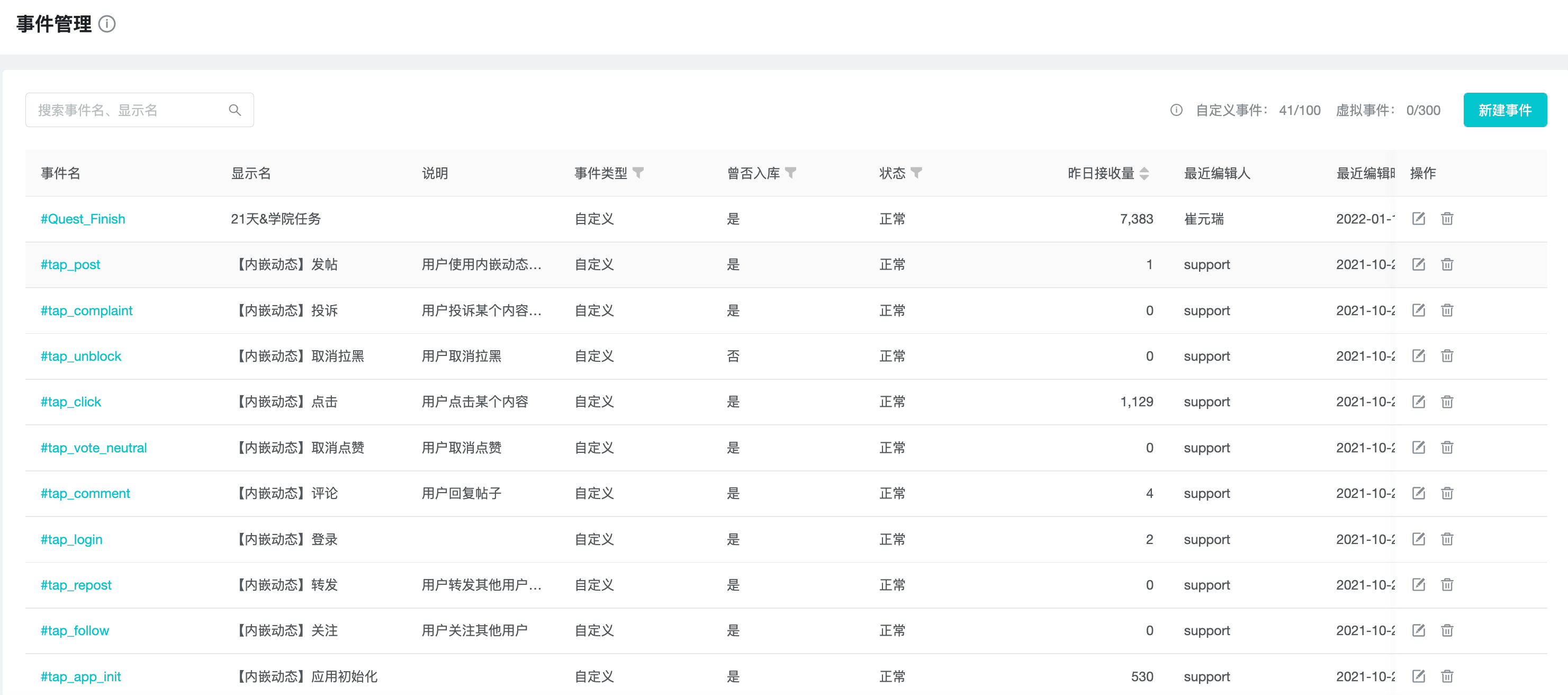
3.1 Concepts Explanation
The "concepts" and "explanations" related to "event" are as follows.
| Concepts | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Event name | Unique identifier of the event. |
| Display name | Display name in the analysis model. |
| Description | Describe the information of buried points, such as: "trigger timing" to help technical staff more accurate buried points; "business connotation" to help business people more in-depth understanding. |
| Event types | Event types are divided into "preset" and "custom" categories: Preset: system built-in events, widely applicable to all kinds of game projects, only need to turn on the buried switch in the SDK to report Custom: custom-created events to meet the personalized needs of game projects, need to be entered in the event management before reporting. |
| Whether to report | Whether the event has been reported. |
| Receive Switch | The switch to receive event reports or not. |
| Status | There are four states: "Normal", "Hidden", "Deleting", and "Deleted". Normal: Events that are in a normal state. Hidden: Not displayed in the analysis model. Deleting: After the reported data is deleted, the event will enter the "Deleting" status, and the deletion can be withdrawn within 72 hours. During this period, the data is still received but not displayed in the analysis model. Deleted: Deleted: After the reported data is finally deleted, the events will be recorded in the metadata management with the status of "Deleted", no more data will be received, no more will be displayed in the analysis model, and the progress of using custom event data will not be occupied. |
| Event properties | You can choose to bind event properties in New and Edit. Event properties are divided into two categories: "preset" and "custom": Preset: The newly created events are in the "debug" state by default and are not displayed in the analysis model. Custom: Customized event properties to meet the personalized needs of game projects . |
| Data limit | To ensure system performance, the number of custom events in "Normal", "Hidden", and "Deleting" states must not exceed 100. "Deleted" custom events do not occupy the usage progress, and you can delete custom events to release the usage progress. |
3.2 Create Custom Events
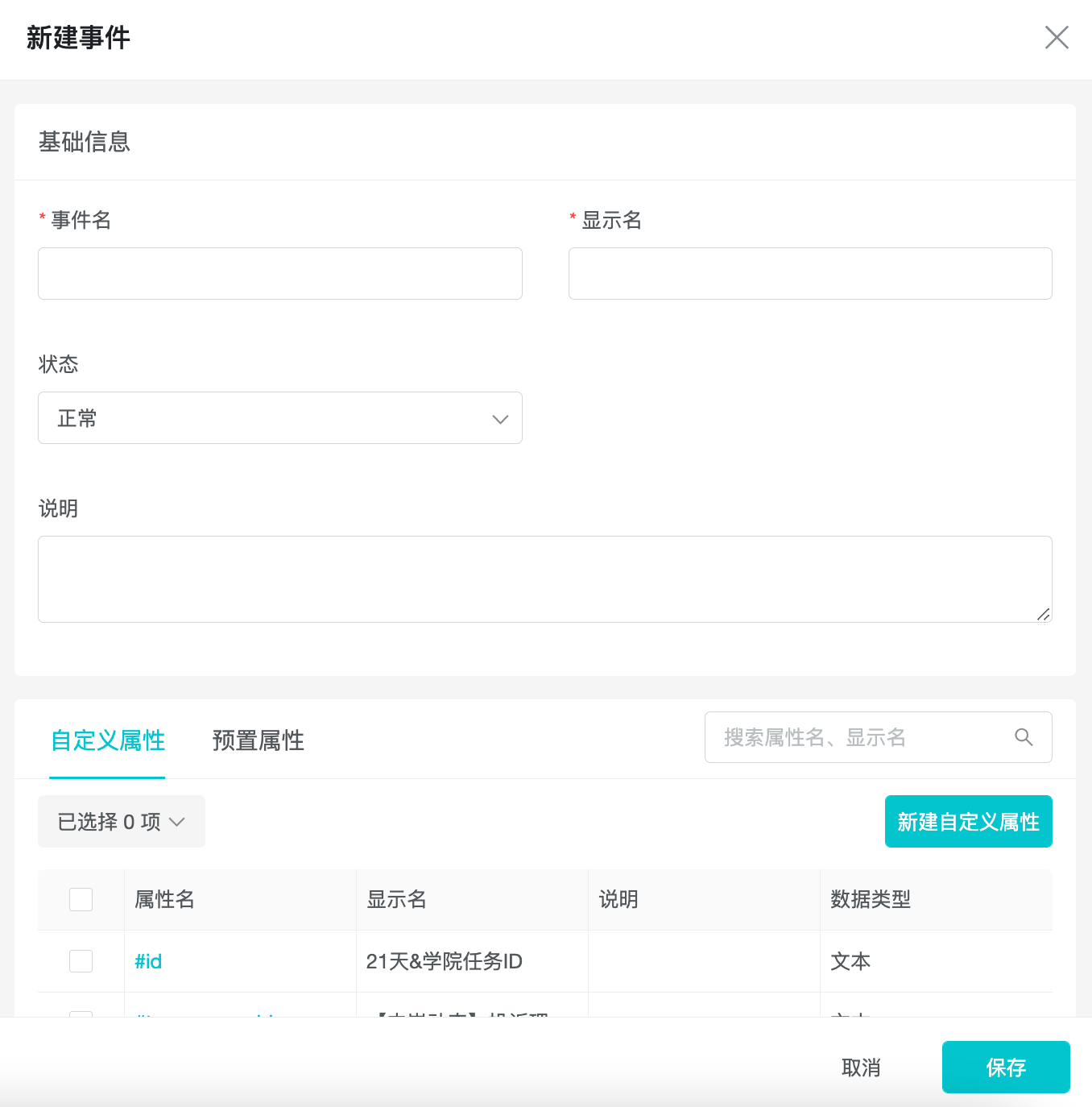
Fill in the basic information. By default, all preconfigured properties are associated, and by default, all custom properties are not associated.
Select the custom properties that need to be associated, create new custom event properties if they do not meet the requirements, and untie the preconfigured properties that do not need to be associated. The creation of custom events is completed.
3.3 View, Edit, Delete Events
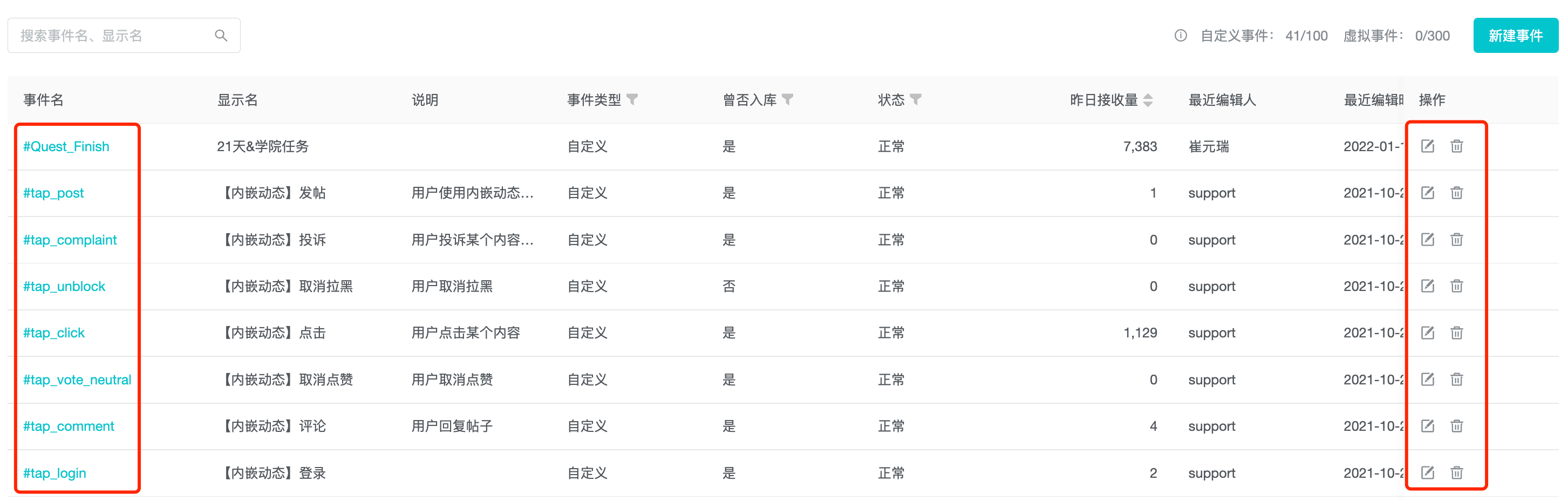
Click on the event name to see the basic information and all associated properties.
In the action bar, you can edit the basic information and change the association with the event properties, but the event name cannot be edited for reported events.
In the action bar, you can delete existing custom events. If a reported event has occurred, it will enter the state of "deleting" and can be revoked within 72 hours. Events that have not been reported will enter the "Deleted" status and will no longer receive data and be displayed in the analysis model, while releasing the progress limit of custom event data usage.
3.4 Q&A
Q1:Why some events are deleted without keeping any records, while some events are deleted and left in the metadata management with "deleted" status?
A1: Events that have not been reported do not keep records, while events that have been reported are kept. During the design process of buried points, business people may change the design of buried points many times due to requirement changes, requirement merging, etc. Therefore, before the act of reporting, it can be considered that all the entry acts are in "draft", while once the data is reported, it is equivalent to the final draft, and we hope that the system can faithfully record all the data collection solutions used in the project.
4. Event Property Management
"Event Attributes" is the attribute information used to describe "events", TapDB has built-in "Pre-set Event Attributes" and provides the function to report "Custom Event Attributes".
In "Event Attribute Management", you can pre-register "Custom Event Attribute" and manage "Event Attribute" from various aspects.
Developers can check the pre-registered custom event attributes that have been reported as "No" and perform buried development.
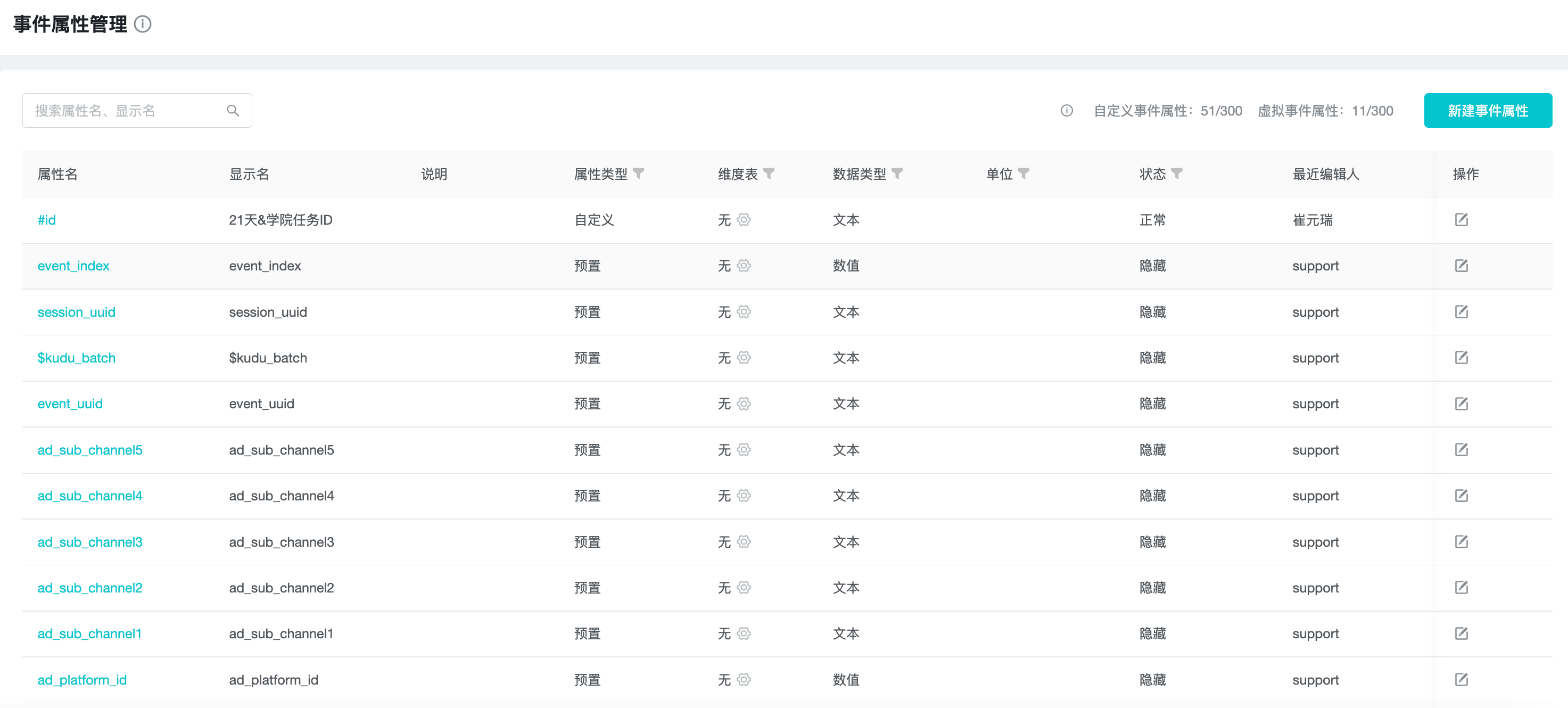
4.1 Concepts Explanation
The "concepts" and "explanations" related to "event property" are as follows.
| Concepts | Explanations |
|---|---|
| Property name | Unique identifier of the event property. |
| Display name | Display name in the analysis model. |
| Description | Describe the attribute information, such as: describe the business connotation, to help business personnel more in-depth understanding. |
| Data types | The data type of the property and the data matching the type can be entered into the library. |
| Units | Units of statistical values, which are displayed in analytical models and reports. |
| Property types | There are two types: "Preset" and "Custom": Preset: built-in event properties, applicable to each event in the game project, only need to turn on the buried switch in the SDK to report. Custom: custom event properties to meet the individual needs of the game project, need to be entered in the event property management before reporting . |
| Whether to report | Whether the event property has been reported. |
| Receive Switch | Switch for the system to receive event properties to report or not. |
| Status | There are two types: "Normal" and "Hidden": Normal: Events that are in a normal state Hidden: not shown in the individual analysis models. |
| Data limit | To ensure system performance, the number of custom event properties should not exceed 300. |
4.2 Create Event Property
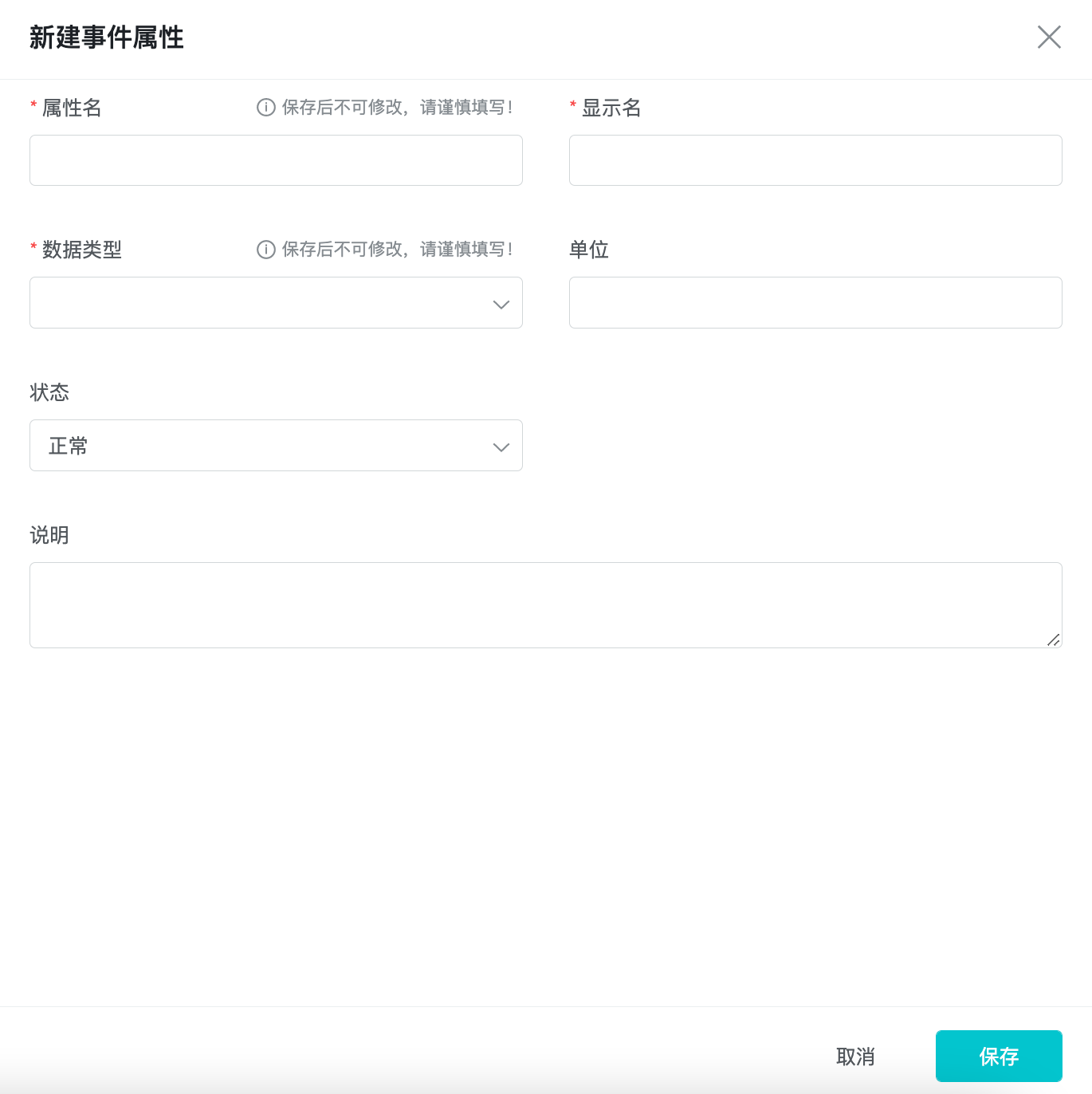
Fill in the basic information about the event property, which completes the creation of a custom property. You can associate it with an event in Event Management.
4.3 View and Edit
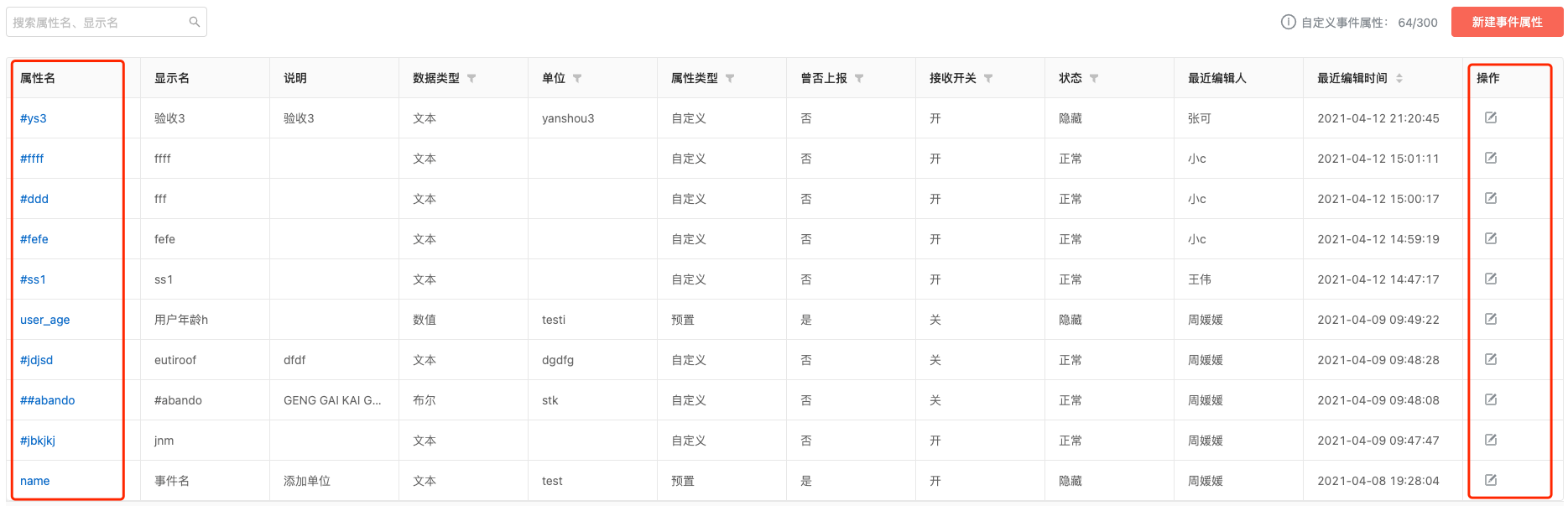
Click on the property name to see basic information and all associated events.
In the action bar, you can edit other basic information except "Property name" and "Data type".
4.4 Q&A
Q1: Why is it not possible to delete a custom event property without reporting any data, but custom events can be deleted?
A1: Adding a new event is just a single record in the table, while adding a new property requires adding a new column in the table, which changes the data structure. Both are very difficult to implement. Therefore, the ability to delete custom attributes is not supported in the current version, and this feature will be added in the future version.
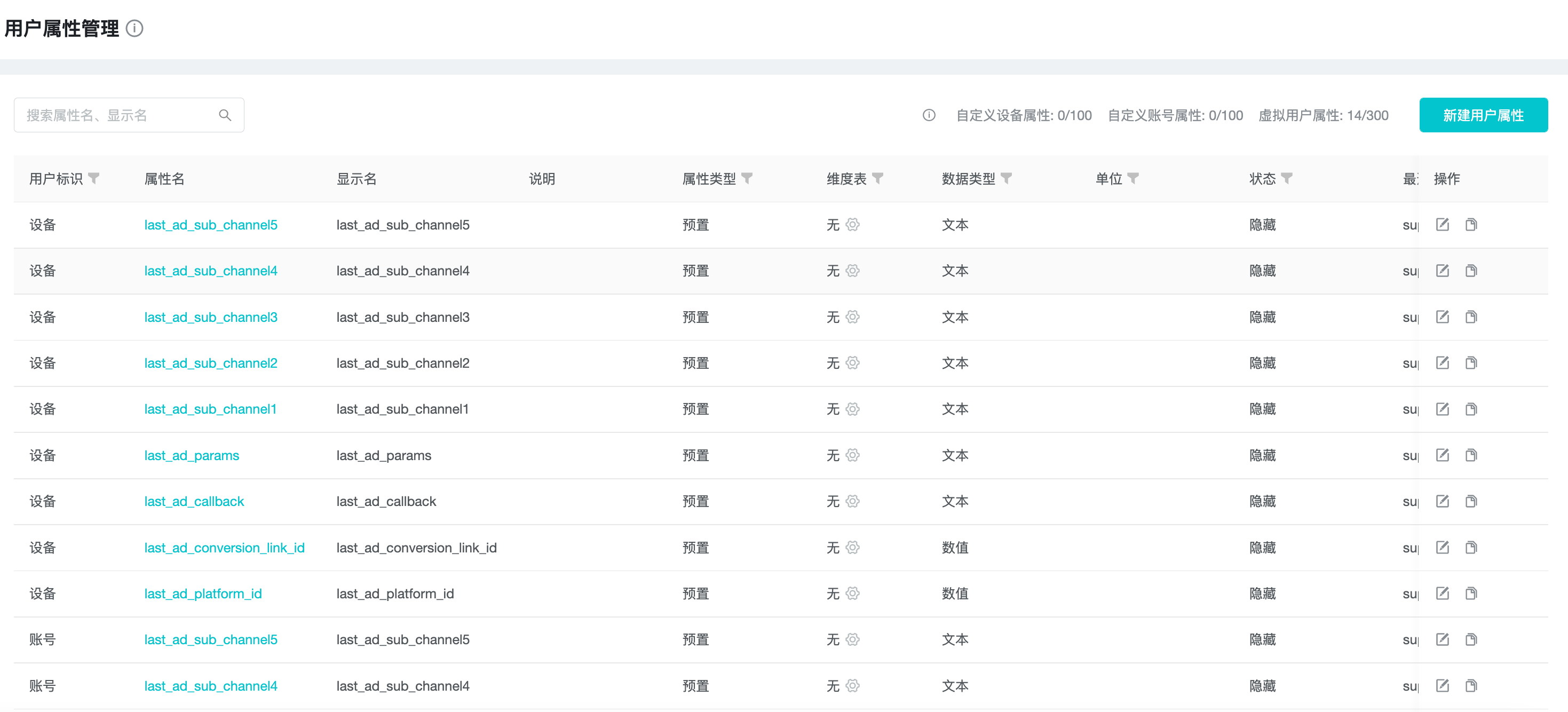
5. User Property Management
"User attributes" is used to describe the attribute information of "user", TapDB has built-in "preset user attributes" and provides the function of reporting "custom user attributes".
TapDB uses "Account" and "Device" as user identifiers to analyze different subjects respectively, and "Account" and "Device" will be used as part of user identifiers in user attribute management respectively.
In the "User Attribute Management" function, you can pre-register "custom user attributes" and manage "user attributes" from various aspects.
Developers can check the pre-registered custom user attributes that have been reported as "No" and perform buried development.
5.1 Concepts Explanation
The "concepts" and "explanations" related to "user property" are as follows.
| Concepts | Explanations |
|---|---|
| User ID | One of the identifiers of user properties, divided into two categories: "Account" and "Device". |
| Property name | One of the identifiers, which together with the "User ID" form a unique identifier. |
| Display name | Display name in the analysis model. |
| Description | Describe the attribute information, such as: Describe the trigger timing to help technical staff more accurate buried points; describe the business connotation to help business people more in-depth understanding. |
| Data types | The data type of the property and the data matching the type can be entered into the library. |
| Units | Units of statistical values, which are displayed in analytical models and reports. |
| Property types | There are two types: "Preset" and "Custom": Preset: built-in user properties, applicable to each event in the game project, only need to turn on the buried switch in the SDK to report. Custom: custom user properties to meet the individual needs of the game project, need to be entered in the event property management before reporting . |
| Whether to report | Whether the user property has been reported. |
| Receive Switch | Switch for the system to receive user properties to report or not. |
| Status | There are two types: "Normal" and "Hidden": Normal: Events that are in a normal state Hidden: not shown in the individual analysis models. |
| Data limit | To ensure system performance, the number of custom user properties should not exceed 100. |
5.2 Create User Property
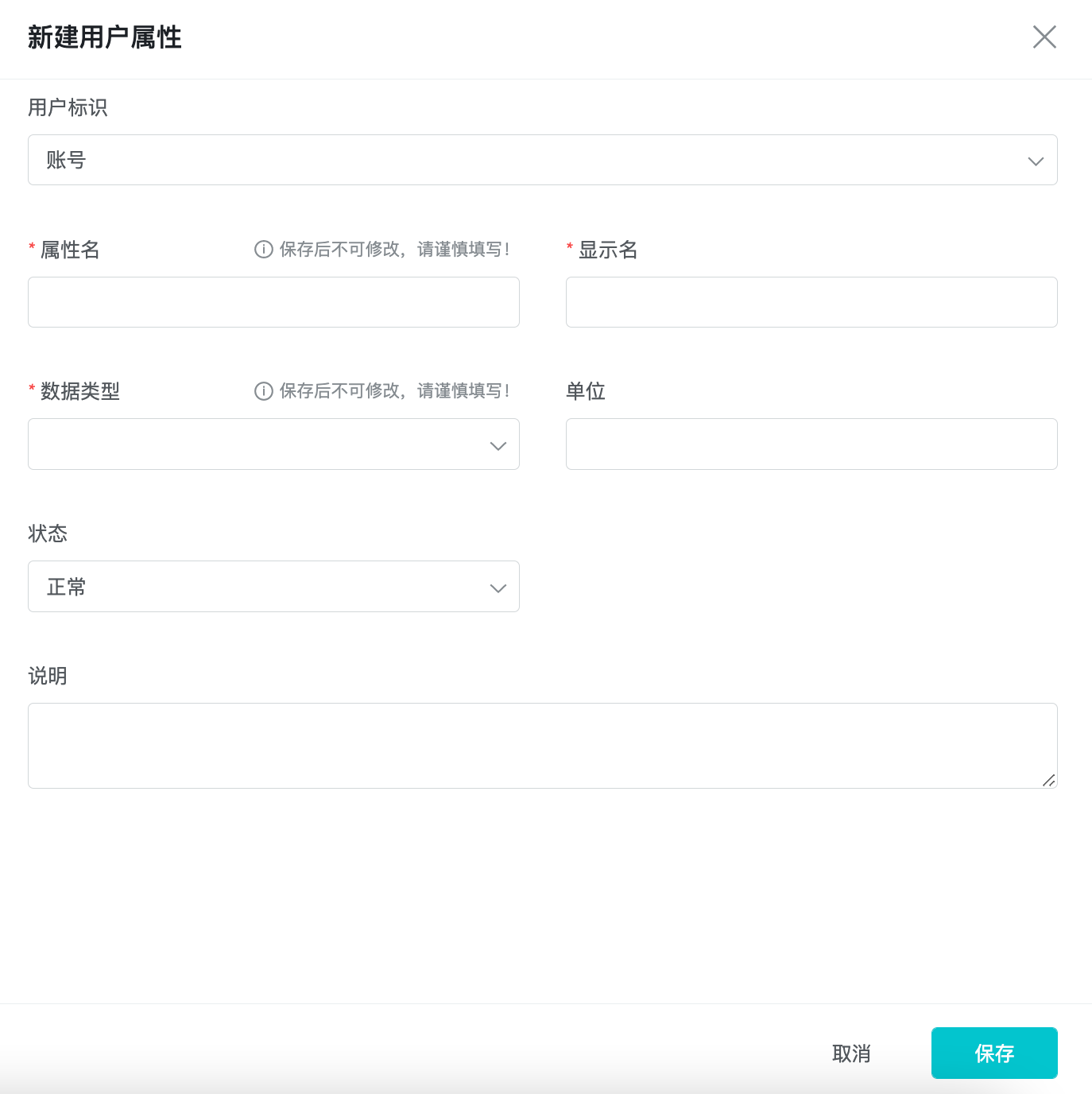
Fill in the basic information to complete the creation of the custom property. Currently, custom user properties cannot be deleted once they are created.
5.3 View, Edit, And Copy
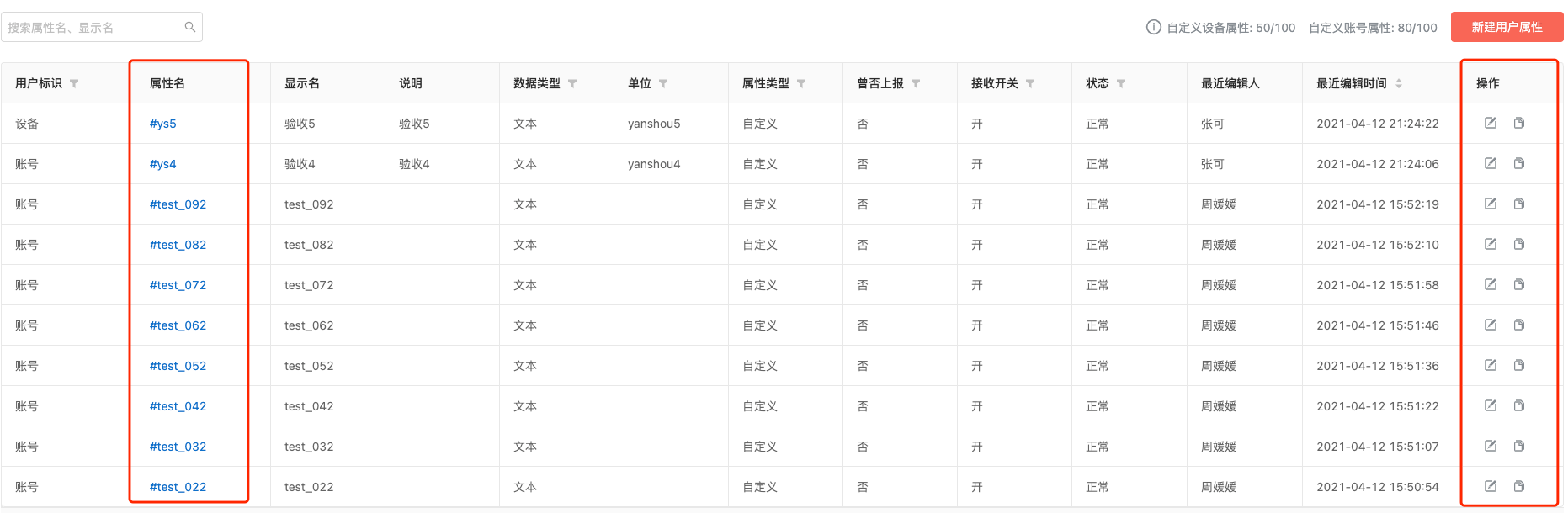
Click the property name to view the basic information.
In the action bar, you can edit the basic information except "property name" and "data type".
In the action bar, you can copy a custom user property with the same information but a different user identity. The copy function is convenient and quick to synchronize the device and account.
5.4 Q&A
Q1: Why is it necessary to distinguish between "device" and "account"?
A1: Identifying users with different subjects is more in line with business needs. For example, in the business of advertising placement, device is a better user identification, while when analyzing users' specific playing behavior, account may be a better user identification. In addition, you can make good use of the copy operation to create user properties for both types of identifiers.