Dimensional Table Properties
1. Overview
For event properties and user properties that have already been reported, the originally uploaded data can be mapped to another presentation or calculated value by uploading a dimension table so that the initial buried property value is not the same as the presentation value.
Compared to virtual properties, dimension table properties can bring in information from outside the system that is not contained in the originally uploaded data, instead of just logical transformation based on data within the system.
2. Applicable Roles and Uses
| Role | Usage |
|---|---|
| Burial Designer (Data Product Manager / Analyst) | Avoid excessive redundant fields in burial design, improve data model paradigm and burial design flexibility |
| Data Analysts (Data Product Managers / Analysts / Operators) | Self-supporting the introduction of external system data as analysis dimensions to meet more personalized analysis needs |
3. Creating Dimension Table Properties
You can create a dimension table property in the "Dimension Table" column of Event Property Management and User Property Management.
Dimension table properties can be created based on preconfigured properties, custom properties and virtual properties, but not the following types of virtual properties.
- virtual attributes created based on dimension table attributes.
- virtual event attributes created based on user attributes.
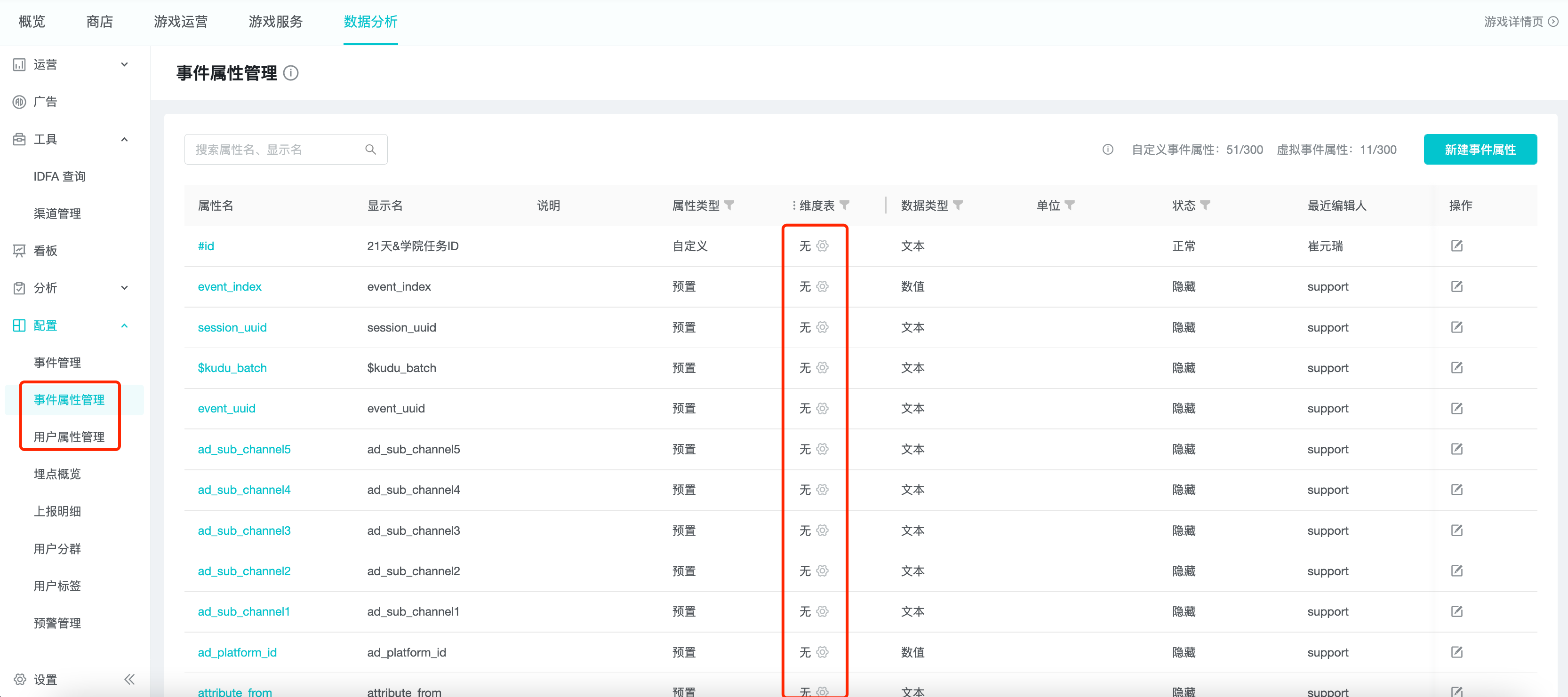
3.1 Uploading
Select the "Upload" dimension table property on the base property field where the dimension table needs to be added.
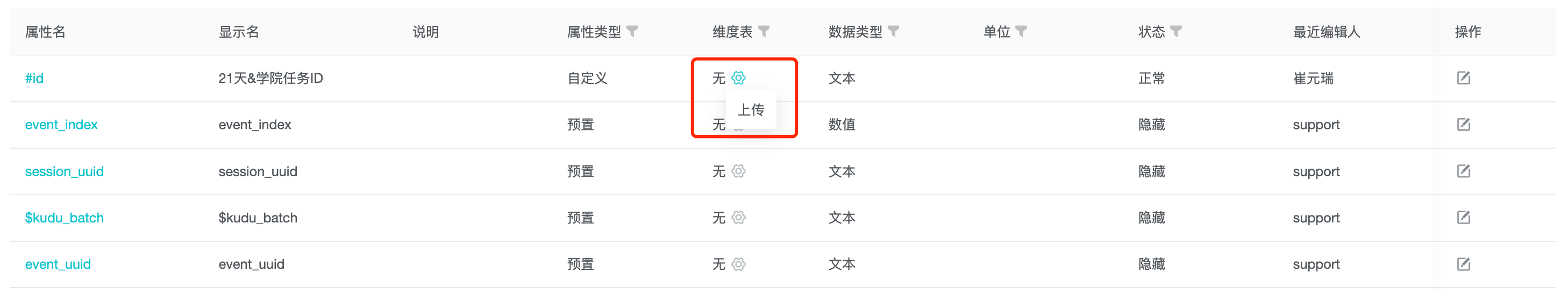
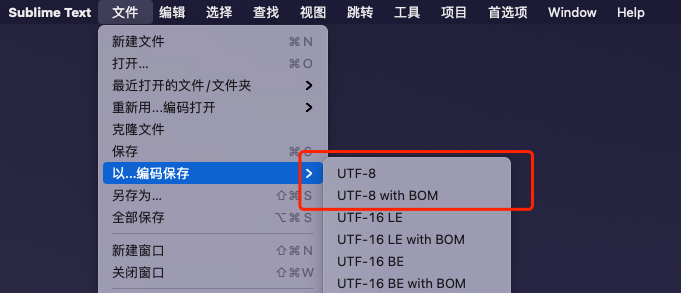
3.2 File encoding requirements
The system supports CSV files in UTF-8 or UTF-8 with Bom encoding format, with a file size of no more than 2G.
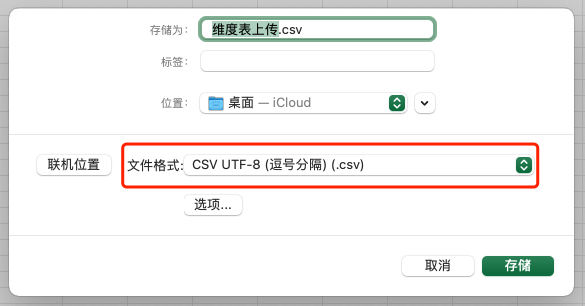
When using Excel, select the "CSV UTF-8 (comma separated) (.csv)" format when saving the document.
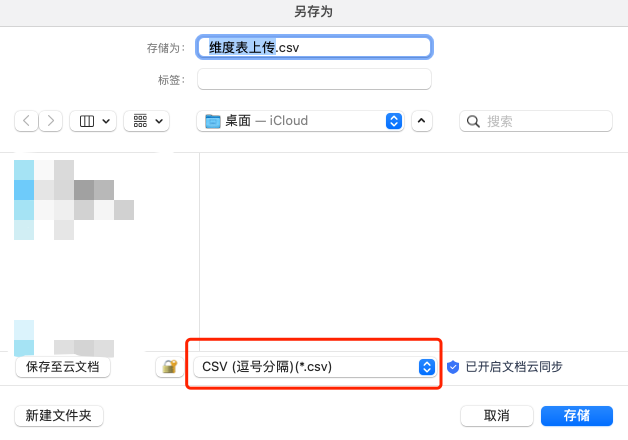
When using WPS, select the "CSV (comma separated) (*.csv)" format when saving the document.
The file can also be saved in UTF-8 or UTF-8 with Bom encoding format using text editing tools such as Sublime, NotePad ++, etc.
3.3 File Format
The first row content will be used as the field name of the dimension table property, which can only contain English, numbers or _, and needs to start with English.
The first column content will be associated with the original attribute, and the first column value needs to correspond to the original attribute value. If duplicate values are encountered, the first column will prevail and subsequent duplicate information will be discarded.
The dimension table properties do not exceed 10 columns, and the content will be adapted to the data type of the property entered, with the following rules.
| selected data type | file content |
|---|---|
| Text | Any content is allowed |
| Numeric | Any number, starting with 0 will remove the 0. |
| time | timestamp, or yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS, yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss, yyyy-MM-dd |
| boolean | true or false |
For rows where the selected data type does not match the file content type, the row will be discarded completely, so please take care to keep the data type consistent.
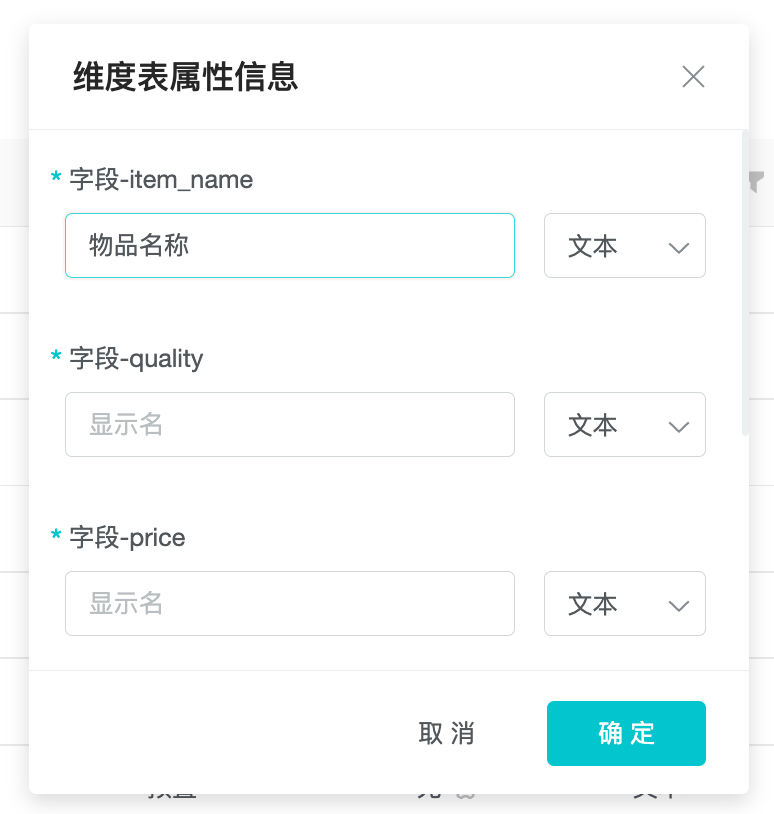
3.4 Fill in the display name and field type
Fill in the display name and data type of the mapped dimension table fields as required.
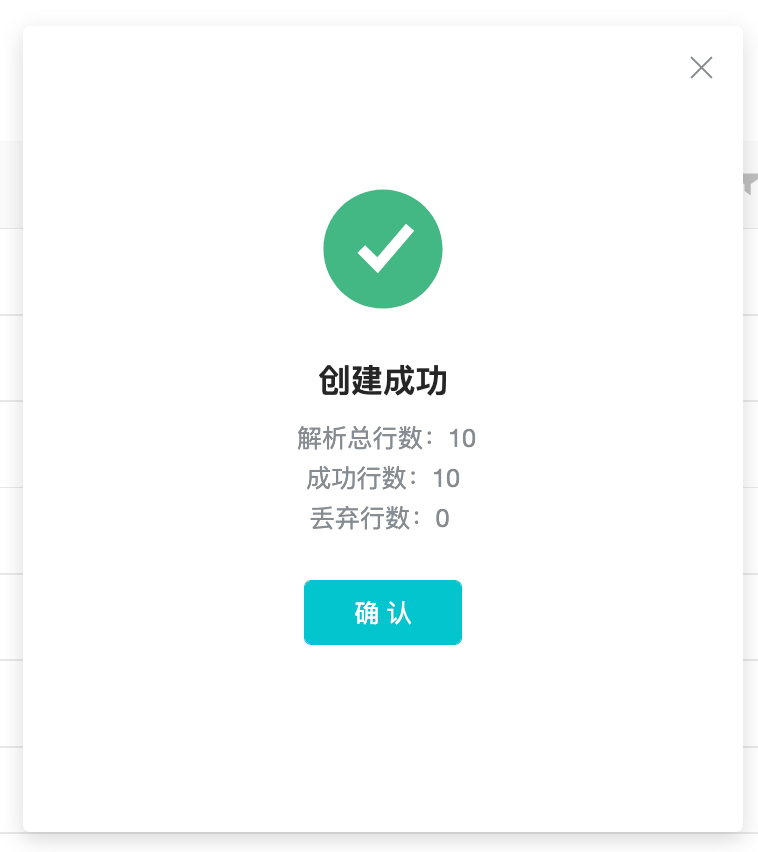
3.5 Parsing Results
Display the total number of rows parsed, the number of successful rows, the number of rows discarded in error and the reason for the error discard.
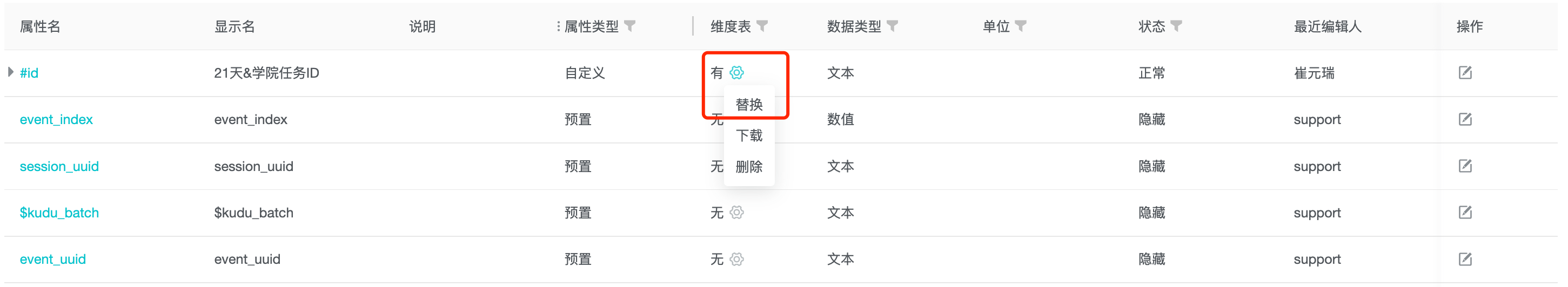
3.6 Replacement
If the parsing result is not as expected, the file can be updated and replaced.
4. Use of dimension table properties
4.1 Managing dimension table properties
Dimension table properties can be managed in the Event Property Management or User Property Management pages.
Dimension table properties are collapsed in the base property column and can be expanded for further manipulation.
! Manage dimension table properties
4.2 Considerations for use in models
Dimension table properties are used in the same way as usual properties, with their calculation logic and filtering conditions determined by their type.
Dimension table properties of event properties can be used in the events associated with their base properties.
Dimension table properties of user properties are used in the same scenarios as general user properties.
5. Best Practice
5.1 Improve buried design flexibility
When collecting users' browsing and ordering information from the game store, only product IDs need to be collected; information such as product names and selling prices can be used to create dimension table properties through "product IDs" to meet analysis requirements.
| Product ID (Base property) | (Dimension table property) | Price (Dimension table property) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Refill Ticket | 50 |
| 2 | World Channel Speakers | 10 |
5.2 Introduction of external information as analysis dimension
The system collects the model information of user devices, combined with the information of the selling price of each model in e-commerce platforms collected through crawlers, so as to get the grade of each model, which is used to identify the value of users.
| Model (basic property) | Price (dimension table property) | User value (dimension table property) |
|---|---|---|
| model_1 | 999 | low |
| model_2 | 1299 | Low |
| model_3 | 1999 | medium |
| model_4 | 4999 | high |